Liver Engraftment / Transplantation
Introduction:
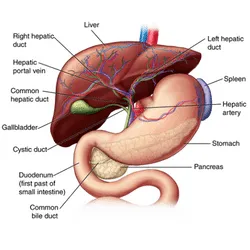
The liver is the solid and largest organ in our body (Filmann et al. 2019). Liver surgery refers to the surgical procedure of removing different parts of the liver. It is also called ‘Hepatectomy’. In this whole process, a complete liver is transplanted in a place of diseased liver. Liver surgery is a very serious and major operation that can be only done by experienced and skilled surgeons (Saito et al. 2020).

The function of a Liver:
The work of the liver is to regulate blood chemicals and emit a product known as ‘Bile’. Bile generally takes away waste products from the liver. The liver processes blood and helps to break down, generate and balance nutrient levels in our body. It also helps to metabolize medicine faster. There are other vital functions of the liver which are given below (Molnar et al. 2019)-
- To convert glycogen from excess glucose for future energy storage.
- To regulate amino acids in blood level which helps to build protein blocks in our body.
- To produce particular proteins for plasma.
- To produce cholesterol and carry out fats.
- To convert toxic ammonia into urea.
- To remove bacteria from the bloodstream.
- To clear ‘Bilirubin’ and generate red blood cells.
- To process hemoglobin to store iron in our bodies.
- To clear toxic drugs and other lethal substances from the blood.
- To regulate blood clotting.
Liver’s Importance in Our Body:
Our liver helps to process blood and break down all the important chemicals and nutrients in our blood cells. The liver changes all those nutrients into a specific form that our body can easily use. In addition, it also regulates our blood chemical levels. That is why the liver is a very important part of our body.
Liver Disease Symptoms:
Symptoms of liver disease may vary from person to person depending on the cardinal cause. However, there are some common symptoms like yellow eyes and skin, pale or black and bloody stool, dark urine, swollen legs or abdomen, nausea, no appetite, vomiting, itchy skin, persistent fatigue and so more (Northup et al. 2021). Apart from these symptoms, there are some specific liver diseases with some specific symptoms which are mentioned below-
Viral Hepatitis:
This specific disease is caused due to inflammation of the liver because of the virus. This is a contagious disease (Dirks et al. 2019).
Symptoms:
- Aching joints and muscles
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Losing appetite
- Fatigue
- Decreased energy
- Pale stool
- Jaundice
Treatment:
Proper vaccination can help to mitigate the risk of Viral Hepatitis.
Fatty Liver:
Fatty liver happens when our liver contains an excess amount of fat. This causes swollen and inflamed liver which can lead to cirrhosis. Cirrhosis can permanently damage our liver. There are two kinds of fatty liver diseases which are 1) Alcoholic fatty liver, and 2) Non-alcoholic fatty liver (Chalasani et al. 2018). Generally, Alcoholic fatty liver disease does not show any symptom on early stage but with time both types can show the following symptoms-
Symptoms for Alcoholic fatty liver:
- Jaundice
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Symptoms for Alcoholic fatty liver:
- Normal weakness
- Fatigue
- Abnormal weight loss
- Losing appetite
- Itchy skin
- Swollen abdomen and legs
Liver Failure:
This can be acute or chronic. It happens in the final stage of any liver disease when the liver is too damaged for functioning. It is a slow process in maximum cases.
Symptoms of chronic liver failure:
- Fatigue
- Appetite loss
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
The last stage of Liver Failure may show the following symptoms:
Symptoms of Acute Liver Failure:
Acetaminophen overdoses can be the reason for acute liver failure. If you have any of the following signs seek medical help immediately.
- Pain in abdomen
- Vomiting
- Confusing
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Always feeling sleepy
- Always unwell
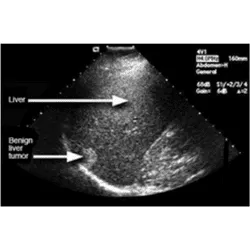
Liver Cancer:
It refers to any cancer that begins from the liver. The two most common type of liver cancer is HCC (Hepatocellular Cancer), and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Nahar and Ara, 2018). Liver cancer develops slowly in your body and does not show any specific symptoms. However, it has some basic symptoms like-
Symptoms:
- Vomiting
- Jaundice
- Itchy skin
- Abdominal pain
- Losing weight
- Easy brushing
- Nausea
These symptoms can easily overlap with other less serious conditions. So, try to take early action if you have any of these symptoms.
Genetic condition:
Common genetic conditions that can cause liver diseases in the future are Hereditary Hemochromatosis, Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and Wilson’s disease (Northup et al. 2021). In this kind of liver disease, symptoms may vary but it can include:
Symptoms:
- Joint pain
- Abdominal pain
- Decreased appetite
- Low energy
- Fatigue
- Jaundice
Autoimmune Symptoms:
In this condition, your weak immune system can attack your liver badly. This condition may include PBC (Primary Biliary Cholangitis), PSC (Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis), and Autoimmune Hepatitis (Peng et al. 2019).
Symptoms of PBC and PSC:
- Jaundice
- Pain in the right abdomen
- Enlarged liver
- Spleen
- Abdomen or leg swelling
- Losing weight
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Chills
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
- Sudden flu
- Decreased Energy
- Fatigue
- Yellow eye and skin
- Joint pain
- Dark urine and pale stool
- Itchy skin
Testing of Liver Related Problems:
Identifying the general cause of liver damage is highly important in case of offering a proper and guiding treatment. At first, the doctor may start with your past medical history and go through some physical tests. After all of these, the doctor may recommend:
Blood Test: The doctor may prescribe some blood tests to ensure liver function and diagnose the disease. This can also help in identifying genetic conditions.

Imaging Tests: CT scan, Ultrasound, and MRI can give an idea about liver damage.
Examining Tissue Samples: Biopsy or removing tissue from the liver can help in identifying any kind of liver disease. This can also help in diagnosing any liver damage. It is done with a long needle inserted through your skin and removes liver tissue for sample testing.

Surgery Types Related to Liver:
There are mainly two types of surgery related to liver cirrhosis or liver tumor. Both are mentioned below:
- Lobectomy and Liver resection:
The procedure of removing surrounding tissues and cancer from your liver is called a Liver Resection. This is only consulted by your surgeon when:
- Your liver is healthy and in the early stage of cancer
- Cancer has not spread into your blood vessels
A liver transplant is only possible in the case of some patients with HCC (Hepatocellular Liver Cancer). You can have a liver transplant when:
- There are less than 3 tumors in your liver
- Each tumor has to be 3cm or less
- Your tumor is not grown in the last three months
Liver transplantation is an abscission/surgical method that restores a malfunctioned or injured liver with a healthy liver from an expired benefactor(donor) or a part of the healthy liver from a living donor. The liver being the most essential and crucial organ of our body as it is responsible for:-
- Decontaminating of matter carried from the intestines, and the concoction of many proteins.
- The main function carried out by the liver is the metabolic process: to mechanize nutrients, medicines, hormones, produces bile in order to absorb fats, cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamins, and break fats in the small intestine during digestion.
- Production of certain proteins for blood plasma and even removes many unwanted chemicals from the body.
Liver diseases are a common matter, but chronic and acute liver illness can lead to liver cirrhosis(a situation where the liver does not function properly and worsens due to chronic injury). There are diversified reasons why liver failure is triggered. People develop cirrhosis of the liver when scar tissues replace normal healthy liver tissues by partially blocking the blood flow eventually resulting in liver malfunction. The main reasons why liver cirrhosis occur so as to why liver transplantation takes place:
- Hepatitis B, C, and D.
- Too much alcohol consumption causes alcoholic liver illness.
- Fatty liver(fat accumulating in the liver) is a cause of liver cirrhosis.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Biliary atresia(diseases affecting the bile duct).
- Genetic disorders affecting the liver which leads to excessive buildup of iron and copper.
In many cases, a person suffering from liver cancer also requires liver transplantation.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs):
Question: What are the types of liver transplants?
Answer: The liver is procured from a deceased donor or a living donor that is explained above in details but another type of liver transplant is:
Domino Liver Transplant: This rare process involves transplanting liver in the body of a patient suffering from end-stage liver disease, the donor being the patient suffering from metabolic disease better known as familial amyloidosis. The donor (having amyloidosis) himself receives a liver from a deceased donor. It is generally expected that the recipient does not develop symptoms of amyloidosis and even if he does it would take decades before the end of natural life expectancy. Doctors usually choose recipients of older age around 55 or more for this type of transplant.
Question: What are the survival rates of the transplant?
Studies have disclosed that survival rates depend on your situation and complicacies but it is noticed that 70%-75% of people who have undergone transplant surgery have a life expectancy of about 5 years which means out of 100 people 75 stays alive for 5 years and the remaining die within 5 years.
Question: Is it possible to live longer for more than 5 years after a liver transplant?
Answer: As estimated by many people about 72% of the candidates are alive even after 5 years of the transplant surgery so there remains a considerable point as to what reasons are responsible that predict the survival chances of a patient. Well, a variety of complicated factors and the patient’s health complications are linked to the surgery because it is almost impossible to forecast an individual’s chances of having a successful transplant surgery and life afterward.
Question: Is transplantation the only treatment after, when everything else has failed?
Answer: The main reason for transplantation is that to remove a malfunctioned liver and replacing it with a healthy liver. In some cases, transplantation is the only treatment to cure a diseased liver as no other machine or medication can reliably perform or function as a liver does.
Question: How to prevent chronic liver disease?
Answer: Following the below guidelines can help you to prevent liver disease to some extent:
- Avoid alcohol and never mix medicines with alcohol
- Vaccinate yourself to fight against hepatitis A and B
- Never consume multiple enzymes or digestive medicines and once you start having digestion issues do visit a doctor
- Try avoiding intravenous drugs unless you need them for other complicated ailments in your body and never share your needles or syringes
- If you are working with some hazardous substance or in some hazardous environment never fail to wash your hands or change your clothes as the intake of those chemicals mistakenly can harm you internally
- Try using your personal care products very carefully and from a recognized brand because if somehow it is consumed the chemicals can be seriously harmful. Never share your personal care cosmetic products.
Question: What are the complications of advanced liver disease?
Answer: The complications are listed below:
- Jaundice
- Stomach infection
- Pleurorrhea
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract
- Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE)
- Swelling of your hands and legs due to an imbalance of fluids in your cells
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
- Hepatorenal Syndrome(HRS)
- Itching due to irritation of sensory nerve ending
- Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis (SBP)
- Hydroperitoneum







 .
.  .
.  .
.